Agarwood, often referred to as oud or agar, is one of nature’s most prized aromatic treasures.
This fragrant resinous wood, derived from the heartwood of the genus Aquilaria tree, has captivated humanity for centuries. With its complex aroma, agarwood has found a place in perfumes, incense, and spiritual practices across cultures, including in countries like Thailand.
But what exactly does agarwood smell like? Let’s unravel the mystery behind its scent and explore its unique characteristics, factors influencing its fragrance, and its myriad uses.
What Does Agarwood Smell Like?
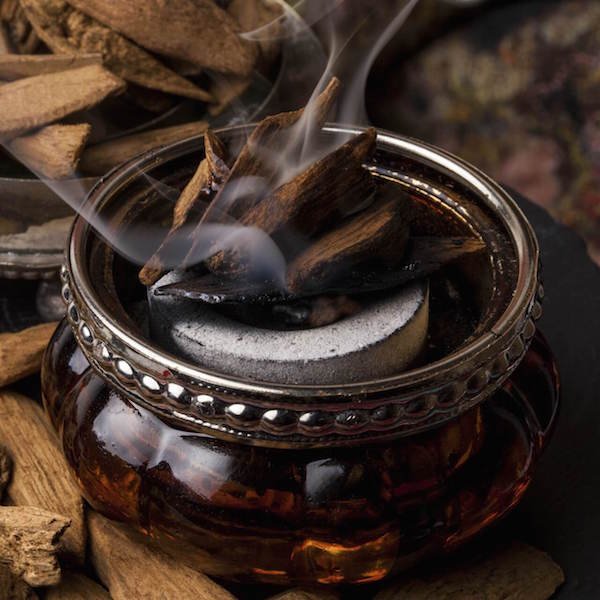

Agarwood, also known as oud, has a rich and complex fragrance that is highly prized for its depth and uniqueness.
Its scent is often described as warm, woody, and resinous, with layers of sweetness, earthiness, and subtle hints of vanilla and musk. Depending on the tree species, resin content, and region of origin, the aroma can also include notes of spice, smokiness, or even floral undertones.
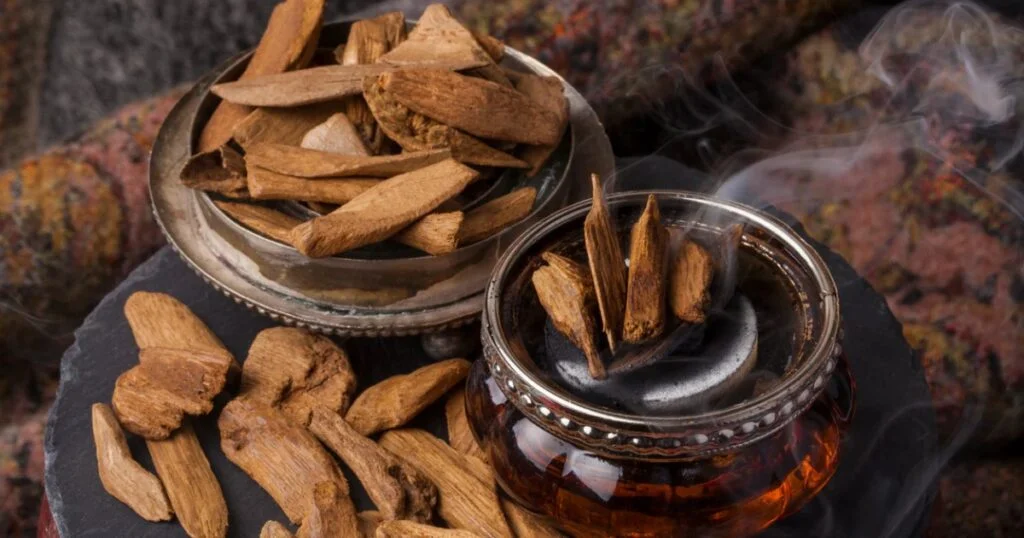
When burned or distilled into oud oil, agarwood releases a luxurious and grounding fragrance. The smoke from agarwood chips is particularly complex, combining deep woody tones with a vanillic sweetness and occasional sandalwood or cedar-like nuances.
Its scent profile varies significantly—Cambodian oud, for example, is known for its sweet and floral characteristics, while Indian varieties may have warmer and spicier tones.
This intricate aroma has made agarwood a staple in luxury perfumery and spiritual practices for centuries. It is cherished for its ability to evoke tranquility and create a deeply immersive sensory experience.
Characteristics of Agarwood’s Fragrance

Sweet and Woody Notes
Agarwood emanates a captivating blend of sweet and woody notes, creating a harmonious fragrance that is both enticing and calming, enhanced by floral notes like jasmine and citrus notes.
The sweet hints intermingle seamlessly with the earthy undertones, evoking a sense of warmth and richness.
These elements combine to form a complex aroma that lingers delicately on the senses, making agarwood a sought-after choice in the world of perfumery and incense crafting.
The woody essence of agarwood adds depth and character to its scent profile, enriched by the warm, balsamic note of myrrh, making it a popular choice for those seeking a unique olfactory experience.
Earthy and Spicy Undertones
Blending seamlessly with its sweet and woody essence, agarwood captivates with earthy and spicy undertones alongside sandalwood. This intricate olfactory profile, characteristic of high-quality agarwood, delivers a profound sensory experience.
The earthy facets evoke images of damp forests, while the spicy nuances add a touch of warmth and depth to the overall aroma. These complex notes, often found in agarwood from Southeast Asia and the Middle East, contribute to the allure and richness of this prized fragrance.
Variations in Scent by Region and Quality
The fragrance profile of agarwood varies widely:
- Cambodian oud: Known for its floral sweetness.
- Indian oud: Offers warm and spicy notes.
- Vietnamese oud: Characterized by deep earthy tones.
The quality also plays a role; higher resin content results in a richer, more intense aroma.
Factors Influencing Agarwood’s Smell

Natural Vs. Synthetic Agarwood
Agarwood is highly prized for its distinctive aroma, but distinguishing between natural forests and synthetic varieties is important.
Natural agarwood, derived from agarwood trees in natural forests, offers a complex scent profile that synthetic versions struggle to replicate. The authenticity of natural agarwood is often tied to its source, such as old-growth forests in Southeast Asia.
Conversely, synthetic agarwood, while more affordable, lacks the depth and richness of natural agarwood’s fragrance. When choosing agarwood products, opting for natural oud oil ensures an unparalleled olfactory experience.
Aging and Resin Content
As agarwood ages, its resin content intensifies, deepening the complexity of its aroma. The resin, produced in response to injury or infection, imbues the wood with its distinctive fragrance.
Oud oil enthusiasts prize well-aged agarwood for its rich and potent scent. The resin content directly influences the depth and longevity of the fragrance, making older pieces highly sought after in perfumery and incense crafting.
This aging process enhances the overall quality and value of agarwood products.
How to Identify Genuine Agarwood By Its Scent?
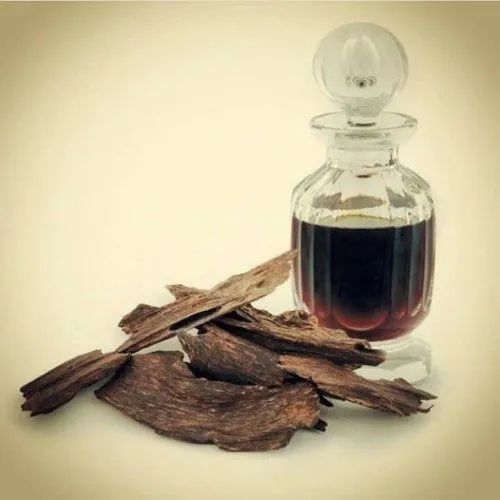

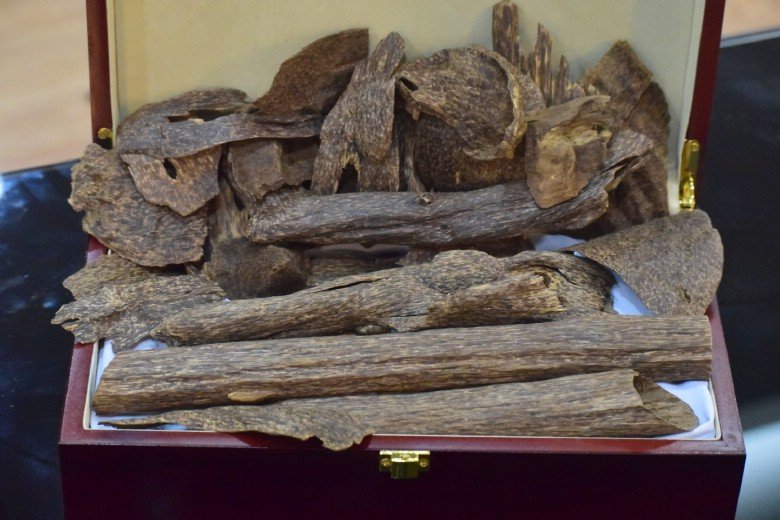
Authentic agarwood has an unmistakable depth that synthetic alternatives cannot replicate. When burned, genuine agarwood chips and this piece of wood emit a smooth, balsamic smoke with no harshness.
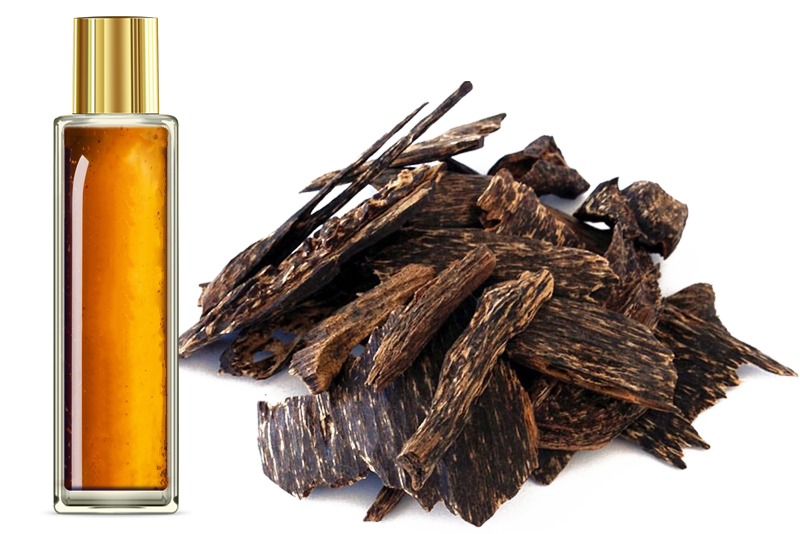
Similarly, pure agarwood oil carries a rich, long-lasting fragrance that evolves over time on the skin.
Uses Of Agarwood For Its Unique Aroma

Perfumes and Incense
Agarwood’s captivating aroma is notably prized in the world of perfumes and incense, often enhanced with patchouli.
Extracted as oud oil, this precious essence, which can be quite expensive at prices reaching several thousand dollars per kilogram, finds its way into a myriad of fragrances and sacred blends, including references found in the bible.
Perfumers intricately weave agarwood’s woody and spicy notes into their creations, offering a luxurious and exotic olfactory experience. Incense enthusiasts seek agarwood incense for its divine and grounding properties, enhancing meditation and spiritual practices.
The rich history and complex aroma of agarwood make it a coveted ingredient in the realm of perfumery and incense crafting.
Aromatherapy and Spiritual Practices
Agarwood holds significance in aromatherapy and spiritual practices, known for its calming and grounding effects.
Utilized in meditation and religious ceremonies, including those in Buddhism, the scent of agarwood is believed to elevate spiritual experiences and promote inner peace.
In aromatherapy, agarwood’s complex aroma is harnessed to reduce anxiety, alleviate stress, and enhance mental clarity.
Its aromatic properties make it a sought-after choice for creating a serene ambiance conducive to spiritual reflection and holistic well-being. In both ancient traditions and modern practices, agarwood plays a vital role in promoting emotional balance and spiritual harmony.
FAQ’s:
Why is Agarwood So Expensive?
The rarity of naturally occurring agarwood makes it one of the most expensive raw materials globally. Overharvesting has led to the depletion of wild Aquilaria trees, further driving up costs.
Does All Agarwood Smell the Same?
Despite its varying scent profiles influenced by region and a wide range of qualities, agarwood does not smell the same across all types. Factors like natural vs. synthetic sources and resin content contribute to the distinct aromas found in different agarwood varieties.
How Long Does the Scent of Agarwood Last?
The captivating scent of agarwood can linger for hours to days, with high-quality varieties lasting longer. Factors like resin content and storage conditions influence its longevity. The rich aroma evolves over time, enhancing its depth and complexity.
Can You Describe the Smell of Burned Agarwood?
The smell of burned agarwood from Vietnam is captivating, releasing a rich and deep aroma. It exudes a mix of sweet, earthy, and slightly spicy notes, creating a warm and soothing ambiance. The scent lingers delicately, leaving a lasting impression.
Conclusion
Agarwood, also known as oudh, is a precious and sought-after aromatic wood that showcases nature’s remarkable ability to produce something truly exceptional.
Its captivating fragrance, often described as the smell of oud, can be experienced in various forms such as essential oils, incense sticks, or as a base note in perfumes, each telling a unique tale of artisanal skill, cultural heritage, and environmental balance.
The process of harvesting agarwood is labor-intensive and requires patience and expertise, especially in the context of sustainable plantation practices. The resin-infused heartwood of Aquilaria trees develops over time in response to certain stressors, resulting in the formation of this highly fragrant mold wood.
Due to its scarcity and the meticulous craftsmanship involved in its extraction, agarwood has become synonymous with luxury and exclusivity in the world of perfumery and aromatherapy.
Beyond its olfactory allure, agarwood holds cultural significance in many regions, including Japan, where it is deeply ingrained in traditions and rituals. Its use dates back centuries, with agarwood being prized for its therapeutic properties and its ability to evoke a sense of tranquility and spirituality.
Moreover, the sustainable harvesting and conservation of the collection of agarwood-bearing trees have gained attention due to the increasing demand for this rare natural resource, which is considered an endangered species of wild fauna and flora that is at risk of extinction in the context of international trade.
Efforts are being made to protect these endangered species while promoting ethical practices within the industry to ensure the longevity of this precious gift from nature.
At Shakomato Farm Organics, we honor this legacy by nurturing sustainable practices that preserve such treasures for generations to come.